LSM110A - MEDINDO ESTADO DE UMA BOIA E ENVIANDO VIA LoRaWAN PARA CHIRPSTACK
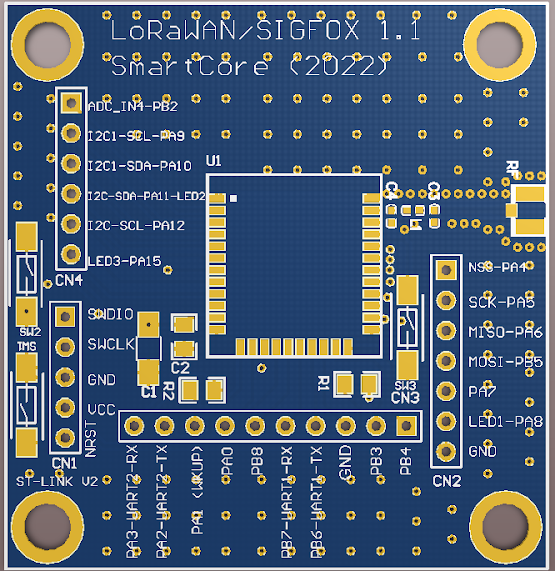
LSM110A Starter KIT
Módulo
O LSM110A é um módulo de última geração que integra o STMicroelectronics STM32WL. É muito menos consumo atual para o dispositivo IoT para estender a vida útil da bateria. E, também suporta ambas as tecnologias – Sigfox e LoRa – com o próprio módulo LSM110A.
O objetivo geral deste BLOG é demonstrar como é possível programar o módulo WISOL LSM110A110A via RAKWIRELESS e assim utilizá-lo como OPENCPU.
O objetivo específico neste projeto é programar o LSM110A para permitir a leitura do estado de uma boia de nível (LIGADO/DESLIGADO) a cada 10s e via OTAA enviar para o servidor CHIRPSTACK via Gateway LoRaWAN da Dragino.
Será enviada a quantidade de vezes que a boia transbordou também.
O que é ChirpStack
ChirpStack é um Servidor de Rede LoRaWAN de código aberto que pode ser usado para configurar redes LoRaWAN. O ChirpStack fornece uma interface web para o gerenciamento de gateways, dispositivos e inquilinos, bem como para configurar integrações de dados com os principais provedores de nuvem, bancos de dados e serviços comumente usados para lidar com dados de dispositivos. O ChirpStack fornece uma API baseada em gRPC que pode ser usada para integrar ou estender o ChirpStack.
REDE LoRaWAN - CHIRPSTACK
Os elementos da CHIRPSTACK são classificados como:
• Endpoints (nós): Os dispositivos responsáveis pela camada de sensoriamento da rede, o endpoint LoRaWAN. Podem coletar informações através de sensores e também acionar dispositivos/máquinas via atuadores. São configurados através de uma das três classes distintas do protocolo LaRaWAN;
• Gateways: Elementos responsáveis por concentrar e processar as informações enviadas pelos endpoints. Os gateways em geral estão conectados a internet, seja por WiFi/Ethernet ou 3G/4G em locais remotos. Mesmo que uma mesma rede LoRaWAN tenha diferentes objetivos, baseados em aplicações distintas, os gateways possuem o objetivo comum de fornecer a maior área de cobertura possível;
• Aplicações: Conectar e interligar os diferentes dispositivos da rede CHIRPSTACK para o fornecimento de informações gerais sobre a coleta de dados dos dispositivos.
CONFIGURAÇÃO AUTENTICAÇÃO NA REDE LoRaWAN
OTAA
• Vantagem: a rede gera e envia as chaves de criptografia; isto torna mais seguro. Devido ao maior nível de segurança, o OTAA é o método mais utilizado em IoT / LoRaWAN.
• AppEUI: Este é um identificador de aplicativo exclusivo usado para agrupar objetos. este
endereço, 64 bits, é usado para classificar os dispositivos periféricos por aplicação. Essa configuração pode seja ajustado.
• DevEUI: Este identificador, configurado de fábrica, torna cada objeto único. Em princípio, esta
configuração não pode ser ajustada.
• AppKey: esta é uma chave secreta compartilhada entre o dispositivo periférico e a rede. É usado para determinar as chaves da sessão. Essa configuração pode ser ajustada.
Concentre-se na OTAA
O Servido de Rede é o componente de software encarregado de estabelecer uma conexão com os objetos e gerenciando o núcleo da rede. Durante a conexão OTAA, e supondo que o dispositivo esteja autorizado a conectar-se a rede, a rede troca chaves de criptografia específicas da sessão com o núcleo da rede. O Servidor de Rede então aloca informações específicas para a sessão e as envia para o aparelho periférico:
• DevAddr: Endereço lógico (equivalente a um endereço IP) que será usado para todos comunicação subseqüente.
• NetSKey (chave de sessão de rede): chave de criptografia entre o objeto e o operador usado para transmissões e para validar a integridade das mensagens.
• AppSKey (chave de sessão do aplicativo): chave de criptografia entre o objeto e operador (através da aplicação) utilizado para as transmissões e para validar a integridade das mensagens
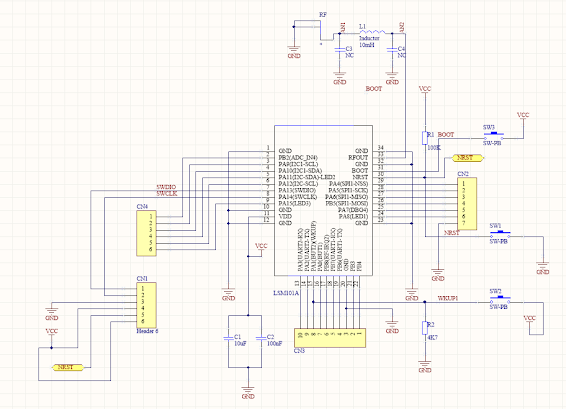
LSM110A e ARDUINO (RAKWIRELESS)
LSM110A é baseado em STM32WL55. No Arduino RAKWIRELESS existe o core similar, o qual deve ser modificado para ser compatível com LSM110A
Baixar RAKWIRELESS Arduino
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RAKWireless/RAKwireless-Arduino-BSP-Index/main/package_rakwireless.com_rui_index.jsonAlterando configurações para ser compatível com o LSM110A
Altere radio_board_if.c para
int32_t RBI_ConfigRFSwitch(RBI_Switch_TypeDef Config)
{
switch (Config)
{
case RBI_SWITCH_OFF:
{
/* Turn off switch */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL1_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL1_PIN, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL2_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL2_PIN, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
break;
}
case RBI_SWITCH_RX:
{
/*Turns On in Rx Mode the RF Switch */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL1_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL1_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL2_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL2_PIN, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
break;
}
case RBI_SWITCH_RFO_LP:
{
/*Turns On in Tx Low Power the RF Switch */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL1_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL1_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL2_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL2_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
break;
}
case RBI_SWITCH_RFO_HP:
{
/*Turns On in Tx High Power the RF Switch */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL1_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL1_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RF_SW_CTRL2_GPIO_PORT, RF_SW_CTRL2_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
break;
}
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
Altere radio_board_if.h para
#define RF_SW_CTRL1_PIN GPIO_PIN_12
#define RF_SW_CTRL1_GPIO_PORT GPIOB
#define RF_SW_CTRL1_GPIO_CLK_ENABLE() __HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE()
#define RF_SW_CTRL1_GPIO_CLK_DISABLE() __HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_DISABLE()
/* official version */
#define RF_SW_CTRL2_PIN GPIO_PIN_13
#define RF_SW_CTRL2_GPIO_PORT GPIOC
#define RF_SW_CTRL2_GPIO_CLK_ENABLE() __HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE()
#define RF_SW_CTRL2_GPIO_CLK_DISABLE() __HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_DISABLE()
Altere Cristal para uso de frequênciais (BAND) mais altas (board.c)
uint8_t BoardGetHardwareFreq(void)
{
uint8_t hardwareFreq = 0;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
/*Configure GPIO pin : PB12 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_12;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStruct);
hardwareFreq = HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_12);
hardwareFreq = 1;
HAL_GPIO_DeInit(GPIOB,GPIO_PIN_12);
return hardwareFreq;
}
Grave com o STM32 Programmer o BOOTLOADER no LSM110A
Assim, pode-se transferir o programa via Serial, através dos pinos PA2 e PA3 do LSM110A.
Ok, o ambiente de desenvolvimento está pronto. Configure 2 parâmetros, os quais deve ser obtidos do servidor CHIRPSTACK.
Use os comandos AT
AT+DEVEUI=9ca7653a4a8bXX15
AT+APPKEY=e6XX867aa4a0dXXf1a5166abff3be9b5
Os demais são HardCoded
Transferindo
Executando
Uma vez gravado o Software, o LSM110A fará o JOIN na LoRaWAN enviará o pacote toda vez que o detectar o transbordo da boia.
CHIRPSTACK
RECEBENDO PACOTES
Código Fonte
//https://docs.rakwireless.com/RUI3/Arduino-API/#settimeout
//https://github.com/beegee-tokyo/RUI3-LowPower-Example/blob/main/RUI3-LowPower-Example.ino
//AT+DEVEUI=9ca7xx3a4axx7515
//AT+APPKEY=e6338xxaa4xxd3af1a51xxabfxxbe9b5
//ATZ
#define DEBUGGER_ON 0
#define LOW_POWER_DISABLE 0
#define OTAA_BAND RAK_REGION_AU915
#define OTAA_DEVEUI {0x00,0x80,0xe1,0x15,0x05,0x1f,0xd8,0x0a}
#define OTAA_APPEUI {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}
#define OTAA_APPKEY {0xa6, 0x14, 0xd5, 0x99 , 0x63 , 0xa0 , 0x86 , 0x1e , 0xdf , 0x27 , 0x02 , 0xae , 0x6f , 0x0e , 0x1a , 0xd6}
/** Time interval to send packets in milliseconds */
uint32_t g_send_repeat_time = 10000;
uint8_t QNT_LINKCHECK_FAIL = 0;
uint8_t QNT_JOINED_FAIL = 0;
uint16_t maskBuff = 0x0002;
uint8_t buff[16];
#include "app.h"
float BAT;
float intpart; // A variable to store the integer part
float floatpart; // A variable to store the float part
bool LINKCHECK_ERROR = 0;
#define ANALOG_BAT PB3
//ATC+SENDCOUNTER=0
//flash
uint8_t flash_value[4] = {0};
bool wr_result = false;
uint32_t data_to_save = 0;
uint8_t flash_read[4] = {0};
uint32_t flash_data = 0;
/** Packet is confirmed/unconfirmed (Set with AT commands) */
bool g_confirmed_mode = false;
/** If confirmed packet, number or retries (Set with AT commands) */
uint8_t g_confirmed_retry = 0;
/** Data rate (Set with AT commands) */
uint8_t g_data_rate = 3;
/** Counter pulse */
uint32_t g_send_counter = 0;
/** Flag if transmit is active, used by some sensors */
volatile bool tx_active = false;
/** fPort to send packages */
uint8_t set_fPort = 2;
/** Payload buffer */
uint8_t g_solution_data[64];
/**
* @brief Callback after join request cycle
*
* @param status Join result
*/
void joinCallback(int32_t status)
{
// MYLOG("JOIN-CB", "Join result %d", status);
if (status != 0)
{
MYLOG("JOIN-CB", "LoRaWan OTAA - join fail! \r\n");
// To be checked if this makes sense
// api.lorawan.join();
// adicionado por Miguel
}
else
{
MYLOG("JOIN-CB", "LoRaWan OTAA - joined! \r\n");
}
}
/**
* @brief LoRaWAN callback after packet was received
*
* @param data Structure with the received data
*/
void receiveCallback(SERVICE_LORA_RECEIVE_T *data)
{
MYLOG("RX-CB", "RX, port %d, DR %d, RSSI %d, SNR %d", data->Port, data->RxDatarate, data->Rssi, data->Snr);
//number of digits on register
if(data->BufferSize==7) {
flash_data = 0;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[0]-'0')*1000000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[1]-'0')*100000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[2]-'0')*10000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[3]-'0')*1000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[4]-'0')*100;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[5]-'0')*10;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[6]-'0')*1;
Serial.print("New Downlink Flash data: ");
Serial.print(flash_data);
Serial.println();
flash_value[0] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 0);
flash_value[1] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 8);
flash_value[2] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 16);
flash_value[3] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 24);
wr_result = api.system.flash.set(0, flash_value, 4);
while (!wr_result)
{
// Retry
wr_result = api.system.flash.set(0, flash_value, 4);
delay(100);
}
//for (int i = 0; i < data->BufferSize; i++)
//{
//Serial.printf("%02X", data->Buffer[i]);
//}
//Serial.print("\r\n");
}
tx_active = false;
}
/**
* @brief LoRaWAN callback after TX is finished
*
* @param status TX status
*/
void sendCallback(int32_t status)
{
MYLOG("TX-CB", "TX status %d", status);
tx_active = false;
}
uint8_t Hall_Sensor = PB8; // pin to measure pulses
void Hydrometer_Pulse()
{
sensor_handler(NULL);
}
/**
* @brief Arduino setup, called once after reboot/power-up
*
*/
void setup()
{
analogReadResolution(12);
Serial.begin(115200);
//Para entrada de comandos apos o reset
delay(10000);
// sensor hall
pinMode(Hall_Sensor, INPUT);
attachInterrupt(Hall_Sensor, Hydrometer_Pulse, CHANGE);
// OTAA Device EUI MSB first
uint8_t node_device_eui[8] = OTAA_DEVEUI;
// OTAA Application EUI MSB first
uint8_t node_app_eui[8] = OTAA_APPEUI;
// OTAA Application Key MSB first
uint8_t node_app_key[16] = OTAA_APPKEY;
if(api.lorawan.appkey.get(buff, 16) == true) {
Serial.print("LoRaWan AppKey = 0x");
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
Serial.printf("%02X", buff[i]);
}
Serial.println("");
} else {
Serial.println("LoRaWan AppKey get fail");
}
////// if (!api.lorawan.appkey.set(buff, 16)) {
////// Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set application key is incorrect! \r\n");
////// return;
////// }
if(api.lorawan.deui.get(buff, 8) == true) {
Serial.print("LoRaWan AppEUI = 0x");
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
Serial.printf("%02X", buff[i]);
}
Serial.println("");
} else {
Serial.println("LoRaWan APPEUI get fail");
}
////// if (!api.lorawan.deui.set(buff, 8)) {
////// Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set device EUI is incorrect! \r\n");
////// return;
////// }
////// if (!api.lorawan.appeui.set(node_app_eui, 8)) {
////// Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set application EUI is incorrect! \r\n");
////// return;
////// }
if (!api.lorawan.band.set(OTAA_BAND)) {
Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set band is incorrect! \r\n");
return;
}
if (!api.lorawan.deviceClass.set(RAK_LORA_CLASS_A)) {
Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set device class is incorrect! \r\n");
return;
}
if (!api.lorawan.njm.set(RAK_LORA_OTAA)) // Set the network join mode to OTAA
{
Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set network join mode is incorrect! \r\n");
return;
}
if (!api.lorawan.rety.set(1)) {
Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set retry times is incorrect! \r\n");
return;
}
if (!api.lorawan.cfm.set(0)) {
Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set confirm mode is incorrect! \r\n");
return;
}
if (!api.lorawan.adr.set(0)) {
Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - set adaptive data rate is incorrect! \r\n");
return;
}
Serial.printf("Set the data rate %s\r\n", api.lorawan.dr.set(2) ? "Success" : "Fail");
Serial.printf("Set channel mask %s\r\n", api.lorawan.mask.set(&maskBuff) ? "Success" : "Fail");
// Setup for LoRaWAN
g_confirmed_mode = api.lorawan.cfm.get();
g_confirmed_retry = api.lorawan.rety.get();
g_data_rate = api.lorawan.dr.get();
// Setup the callbacks for joined and send finished
api.lorawan.registerRecvCallback(receiveCallback);
api.lorawan.registerSendCallback(sendCallback);
api.lorawan.registerJoinCallback(joinCallback);
Serial.printf("RUI3 %s\n", api.system.firmwareVersion.get().c_str());
api.lorawan.linkcheck.set(1);
// Initialize module
Wire.begin();
// Register the custom AT command to get device status
if (!init_status_at())
{
MYLOG("SETUP", "Add custom AT command STATUS fail");
}
// Register the custom AT command to set the send Counter
if (!init_counter_at())
{
MYLOG("SETUP", "Add custom AT command Send Counter fail");
}
// Get saved sending counter from flash
get_at_setting();
// Create a timer.
api.system.timer.create(RAK_TIMER_0, sensor_handler, RAK_TIMER_PERIODIC);
if (g_send_repeat_time != 0)
{
// Start a timer.
api.system.timer.start(RAK_TIMER_0, g_send_repeat_time, NULL);
}
if (g_confirmed_mode)
{
MYLOG("SETUP", "Confirmed enabled");
}
else
{
MYLOG("SETUP", "Confirmed disabled");
}
MYLOG("SETUP", "Retry = %d", g_confirmed_retry);
MYLOG("SETUP", "DR = %d", g_data_rate);
api.system.lpm.set(1);
if (!api.lorawan.join()) // Join to Gateway
{
Serial.printf("LoRaWan OTAA - join fail! \r\n");
return;
}
}
/**
* @brief sensor_handler is a Interrupt function or user call
*/
void sensor_handler(void *)
{
MYLOG("UPLINK", "Start");
//FALLING
if(digitalRead(Hall_Sensor)==LOW)
{
if (api.system.flash.get(0, flash_read, 4))
{
flash_data |= flash_read[0] << 0;
flash_data |= flash_read[1] << 8;
flash_data |= flash_read[2] << 16;
flash_data |= flash_read[3] << 24;
}
flash_data++;
//Overflow Register
if(flash_data==9999999)
flash_data++;
flash_value[0] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 0);
flash_value[1] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 8);
flash_value[2] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 16);
flash_value[3] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 24);
wr_result = api.system.flash.set(0, flash_value, 4);
}
// Create payload
char value = 0x31;
for (int idx = 0; idx < 7; idx++)
{
g_solution_data[idx] = value;
value++;
}
// BAT = (analogRead(ANALOG_BAT) * 3.0) / 4096.0; //CR
BAT = (analogRead(ANALOG_BAT) * 3.3) / 4096.0;
Serial.println(BAT);
intpart = floor (BAT); // Get the integer part by rounding down
floatpart = fmod (BAT, intpart); // Get the float part by calculating the remainder
g_solution_data[0] = flash_value[0];
g_solution_data[1] = flash_value[1];
g_solution_data[2] = flash_value[2];
g_solution_data[3] = flash_value[3];
g_solution_data[4] = intpart;
g_solution_data[5] = floatpart*100.0;
g_solution_data[6] = digitalRead(Hall_Sensor);
// Send the packet
send_packet();
}
/**
* @brief Send the data packet that was prepared in
* Cayenne LPP format by the different sensor and location
* aqcuision functions
*
*/
void send_packet(void)
{
Serial.println(flash_data);
if (!api.lorawan.njs.get())
{
MYLOG("UPLINK", "Not joined, skip sending");
QNT_JOINED_FAIL++;
if(QNT_JOINED_FAIL==3)
{
QNT_JOINED_FAIL=0;
//api.system.reboot();
}
return;
}
// Check if it is LoRaWAN
MYLOG("UPLINK", "Sending packet...");
// Send the packet
api.lorawan.linkcheck.set(1);
Serial.printf("Set channel mask %s\r\n", api.lorawan.mask.set(&maskBuff) ? "Success" : "Fail");
if (api.lorawan.send(7, g_solution_data, set_fPort, g_confirmed_mode, g_confirmed_retry))
{
MYLOG("UPLINK", "Packet enqueued, size 7");
tx_active = true;
}
//linkcheck fails 3 times
if(LINKCHECK_ERROR==true)
{
LINKCHECK_ERROR=false;
QNT_LINKCHECK_FAIL++;
if(QNT_LINKCHECK_FAIL==3)
{
QNT_LINKCHECK_FAIL=0;
//api.system.reboot();
}
}
}
/**
* @brief This example is complete Interrupt Sensor (GPIO)
* driven. The loop() does nothing than
* sleep.
*
*/
void loop()
{
api.system.sleep.all();
}
Compilação
UPLINK
Status do Transbordo ou não
DOWNLINK para inicializar contador de Transbordos
Exemplo (BASE64)
MDAwMDExMQ== ---> 0000111 transbordos
/**
* @brief LoRaWAN callback after packet was received
*
* @param data Structure with the received data
*/
void receiveCallback(SERVICE_LORA_RECEIVE_T *data)
{
MYLOG("RX-CB", "RX, port %d, DR %d, RSSI %d, SNR %d", data->Port, data->RxDatarate, data->Rssi, data->Snr);
//number of digits on register
if(data->BufferSize==7) {
flash_data = 0;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[0]-'0')*1000000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[1]-'0')*100000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[2]-'0')*10000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[3]-'0')*1000;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[4]-'0')*100;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[5]-'0')*10;
flash_data = flash_data + (data->Buffer[6]-'0')*1;
Serial.print("New Downlink Flash data: ");
Serial.print(flash_data);
Serial.println();
flash_value[0] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 0);
flash_value[1] = (uint8_t)(flash_data >> 8);
Detectado pelo Downlink
LOW POWER
Init
void loop()
{
api.system.sleep.all();
}
Dúvidas sobre o código fonte
suporte@smartcore.com.br
Sobre a SMARTCORE
A SmartCore fornece módulos para comunicação wireless, biometria, conectividade, rastreamento e automação.
Nosso portfólio inclui modem 2G/3G/4G/NB-IoT/Cat.M, satelital, módulos WiFi, Bluetooth, GNSS / GPS, Sigfox, LoRa, leitor de cartão, leitor QR code, mecanismo de impressão, mini-board PC, antena, pigtail, LCD, bateria, repetidor GPS e sensores.
Mais detalhes em www.smartcore.com.br



















Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário